Muhammad: Origins of Islam:
The Pre-Islamic World
“Above all the two empires faced the challenge of each other.… At stake was not merely Byzantine versus Sasanian political control and economic influence, but also Christianity as opposed to Zoroastrianism and Hellenic as opposed to Iranian cultural traditions.” —Fred M. Donner, Muhammad and the Believers.
A Time of Conflict
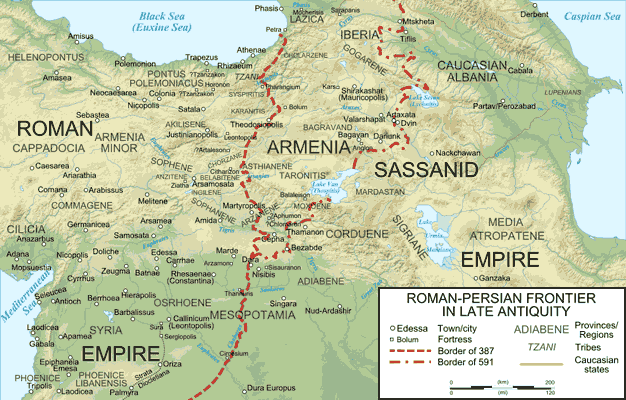
By 570 CE, the year of Muhammad’s birth, two major powers of the region, the Eastern Roman Byzantine Empire and the Sasanian Empire, were locked in a series of intense debilitating wars with each other. These recurred throughout the sixth and seventh centuries and contributed to the demise of both civilizations.
From their capital, Constantinople, the Byzantine emperors of the sixth century had envisioned and attempted a Christianized form of the Roman world order. But this dream proved impossible as pagans, Jews, and Samaritans resisted Christianity. Within Christianity itself sharp divisions arose, particularly about the human and/or divine nature of Jesus that set one group against another. Ascetic movements: monasteries, convents, pilgrimages, saint worship, icons, relics and new forms of liturgy affected the religious mood of the Empire, and a widespread appeal of apocalyptic ideas predicting the end of days ran rampant.
In the fourth and fifth centuries much of the western half of the Byzantine Empire was disintegrating, unable to maintain the strength and prosperity of so vast a territory. Though undermined by earthquakes and repeated bouts of plague, the eastern half of the empire remained intact.
Zoroastrianism became the state religion of the Sasanian Empire in the third century. But the population included large communities of Jews, some established in Babylon as far back as the time of the Babylonian Exile in 597 BCE and of the later Great Revolt in 70 CE. Though the Sasanids were suspicious of Roman Christianity, Christian communities like the Nestorians, who had been condemned at the Council of Ephesus in 431 and forced to flee the Byzantine Empire (the Old Roman Empire), were favored.
In the fourth and fifth centuries much of the western half of the Byzantine Empire was disintegrating, unable to maintain the strength and prosperity of so vast a territory.
Fred M. Donner writes in Muhammad and the Believers, “For all their differences, the Byzantine and Sasanian empires shared certain common features and faced similar challenges. Their rulers struggled to unify vast domains and fragmented populations by the use of force, when necessary, and by recourse to a religious ideology that they tried to impose on their subjects, which bolstered their claim to rule. Both, perhaps inadvertently, fostered movements with egalitarian tendencies that used religious ideas to blunt the harshness of existing social norms. Both faced the challenge of warding off external enemies on their frontiers … Above all the two empires faced the challenge of each other. … At stake was not merely Byzantine versus Sasanian political control and economic influence, but also Christianity as opposed to Zoroastrianism and Hellenic as opposed to Iranian cultural traditions.”
Tribal Society and Trade
The predominance of vast barren desert, alleviated only by a few water sources where agricultural communities gathered, such as Ta’if and Yathrib, made complete colonization unattractive.
Most of the Arabian Peninsula remained outside the direct control of these two world powers. The predominance of vast barren desert, alleviated only by a few water sources where agricultural communities gathered, such as Ta’if and Yathrib, made complete colonization unattractive. Nevertheless, both empires competed to establish alliances with tribes via barter and bribery as they tried to control trade routes.
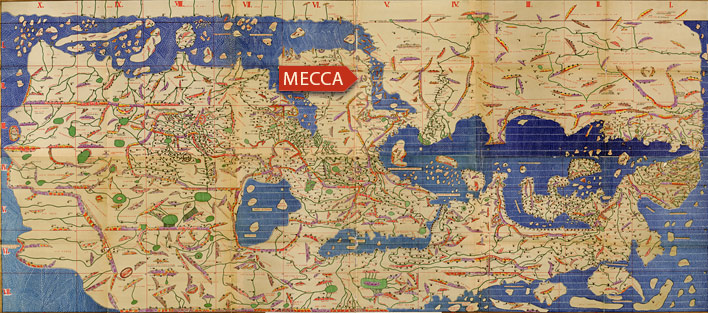
Competitive efforts from both empires centered particularly on Yemen in the south. There, agriculture thrived due to an ancient irrigation system of large water tunnels in the mountains, and dams, the most impressive of which was known as the Ma’rib Dam, built ca. 700 BCE. The ancient states of Saba, Ma’in, Qataban, Hadhramaut, Awsan, and Himyar evolved in this region, thanks to the cultivation and trade of spices and aromatics, including frankincense and myrrh, highly valued by the surrounding cultures. The Mar’rib Dam collapsed in 570 CE. This is noted in the Qur’an and the consequent failure of the irrigation system provoked the migration of up to 50,000 people, who were forced to survive the harsh environment, taking refuge with other tribes as they were able.
Too few resources led to endless battles with other tribes for water, pastureland and grazing rights.
The sixth century saw Bedouin tribes on well-saddled camels employed by foreign merchants to transport goods and guide caravans from one well to another by direct route across the steppes. Thus goods from India, East Africa, Yemen and Bahrain traveled on to both Byzantium and Syria.
Nomadic (badawah) life was harsh. Scarce resources meant that survival depended upon close-knit family and kinship groups or “tribes.” Too few resources led to endless battles with other tribes for water, pastureland and grazing rights. A tribe’s sheep, goats, horses, camels and slaves were under constant threat from an acquisition raid, or ghazu. The ghazu was a form of negative reciprocity and an accepted part of life necessitated by the fact that there was simply not enough to go around, particularly when water holes dried up and all food sources failed. These kinds of raids had become endemic during the century preceding Muhammad’s revelation and often escalated from quarrels into decades of warfare between tribes. The Days of al-Fijar, in which the Quraysh and the Kinanah opposed the Hawazin, is an example of this, and the young Muhammad, who was a member of the Quraysh from the distinguished clan of Hashim, is said to have participated.
To facilitate retribution a “blood money” value was set for everything: individuals, goods and assets.
To be successful a tribe needed members who would not be defeated by the overwhelming harshness of life in the arid desert. As a consequence each tribe’s life and culture evolved around a chivalric code (muruwah) that was an attempt to overcome life’s severe conditions, give meaning to the Arab’s world and prevent people from giving in to despair. “Muruwah meant courage, patience, endurance; it consisted of a dedicated determination to avenge any wrong done to the group, to protect its weaker members, and defy its enemies. To preserve the honor of the tribe, each member had to be ready to leap to the defense of his kinsmen at a moment’s notice and to obey his chief without question. … Above all, a tribesman had to be generous and share his livestock and food. … A truly noble Bedouin would take no heed for the morrow, showing by his lavish gifts and hospitality that he valued his fellow tribesmen more than his possessions…,” says Karen Armstrong in Muhammad A Prophet of our Time. Struggle was glorious, arrogance a sign of nobility and humility a sign of weakness.
Within the tribe the Law of Retribution was arbitrated and administered by the chief, or sheykh: injured parties could claim retribution—an act of aggression would be avenged in equal terms—the killing of a neighbor’s son or camel meant the execution of one’s own son or camel. To facilitate retribution a “blood money” value was set for everything: individuals, goods and assets.
In an age where outside the tribe the individual was totally vulnerable, it was the idea of hospitality (diyafah) that enabled travel through tribal territories. Writes Paul Wheatley in his book The Places Where Men Pray Together: Cities in Islamic Lands Seventh Through Tenth Centuries, “Arabian tribesmen view hospitality as a sacred duty; the pagan poets of the Jahiliya praised it as a cardinal virtue and archetyped it in the celebrated legend of Hatim al-Ta’I. Elaborate rules governed the granting and termination of hospitality to persons outside the lineage, doubtless in response to the functional significance of the traveller.” Wheatley goes on to say that providing protection and safe conduct to strangers displayed the authority of the sheykh and his tribe and confirmed their control over the territory.
External Stories and Videos

The Legend of Hatim al Tai
This classic tale illustrates the Arab’s view of hospitality as a sacred duty and cardinal virtue—in this retelling the reader is also invited to reflect upon the real meaning of generosity.
