
Mesopotamia:
“The Land Between Two Rivers”
Dûrzan Cîrano, Wikimedia Commons
Part of the Fertile Crescent, Mesopotamia (“the land between two rivers” in Greek) was by its geographical location and development influential in the region from at least 2500 BCE to the fall of Babylon in 539 BCE.
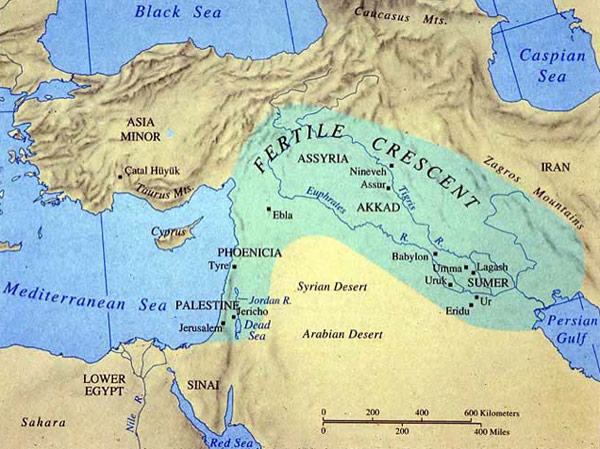
The rise of Mesopotamia stemmed, in part, from a geographical quirk. Unpredictable amounts of silt-laden water caused by the disastrous seasonal flooding of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers had to be controlled. Consequently, people learned how to construct levees and to develop a system of irrigation canals. Adapting and improving on these skills, they were able to build settlements, city-states and temples. Within high walls for safety, city-dwellers developed complex hierarchical cultures, whose influence was felt from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean, from Iran to Syria, Palestine and Asia Minor. We know of the ancient Mesopotamian empires of Sumer, Assyria and Babylon through their extant written records that, for the first time in our history, enabled scholars to do more than infer and speculate from archeological findings.
The Elamites of southeastern Iran and the Semites of Ebla in Syria both borrowed their script and, in part, their languages from Mesopotamia in the third millennium; as did the Semites, the Hurrians of Syria-Palestine and the Indo-Europeans of Anatolia, known as the Hittites, in the second. The courts of the Near East in the fifteenth century BCE were in Egypt at el-Amarna, but they wrote in cuneiform script in the Akkadian language, which was the regional language of diplomacy. Over 300 tablets, known as “the Amarna Letters” have been found which include correspondence from both Amenhotep III’s and Akhenaten’s reign that have helped to establish the history and chronology of the period.
The Mesopotamian’s mythological, epic and poetic literature, and their scientific works travelled from Babylonia throughout the then-known world. Egypt borrowed its astrology from Babylonia in the first millennium. Themes and stories developed in Mesopotamia are found in the Old Testament Bible. Thales of Miletus used Babylonian records of solar observations to become the first to predict a total solar eclipse. Even the formation of Greek philosophical thought appears to have stemmed from Babylon as its literature spread from Asia Minor to the Aegean and on to the Greek islands.

The oldest city found to date is Uruk (ca 3900 BCE), located near the Euphrates River about 155 miles south of Baghdad. Uruk was a capital city for the Akkadian, Sumerian, Babylonian, Assyrian, and Seleucid civilizations and was abandoned only after 100 CE. In the late fourth millennium it was the largest city in the Sumerian civilization, and by 2900 BCE it included nearly 1,000 acres, making it most likely the largest city in the world at the time, with somewhere in the region of 50,000–80,000 residents. Along with urban settlements were temples, platforms, ziggurats, and cemeteries, all enclosed by a massive wall almost ten kilometers in circumference which was said to have been built on the orders of King Gilgamesh, who, well known in stories and legends, may actually have been an historical king of Uruk around 2700 BCE.

More than 200,000 cuneiform clay tablets have been found in the lands of ancient Mespotamia. Tablets with pictographic script from about 3000 BCE were found in the ruins of the Red Temple of Uruk. Nearly 30,000 cuneiform tablets (dated about 2350 BCE) were recovered at Telloh, near Lagash. Many others were found at a temple library at Nippur (2500 BCE), south of modern Baghdad. The Great House of Tablets, which seems to have been a law library dating to the reign of Ur-Nammu around 2100 BCE, was unearthed in the ruins of Ur.
Although four-fifths of the tablets found were accounts of everyday business transactions, obligations and inventories, a large number were devoted to astronomy including accurate calculations; to mathematics (arithmetic, geometry and algebra) which was very well developed from the first half of the second millennium; to jurisprudence, such as the famous Hammurabi Code; and to diagnostic medicine.
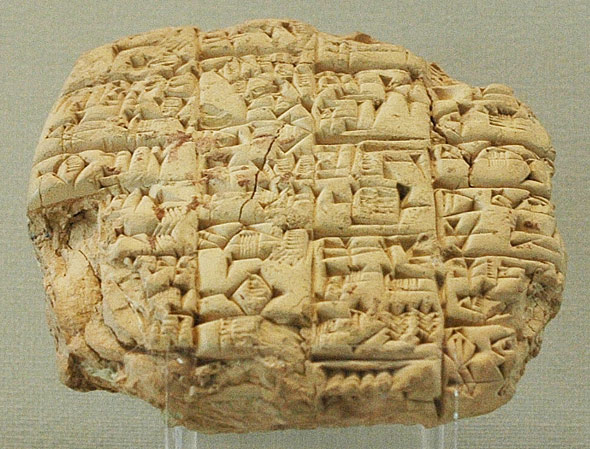

Mesopotamians invented not only writing but may well have introduced several technologies including metal- and copper-working, glass and lamp making, textile weaving, flood control, water storage, and crop irrigation.

Wooden game-board from Royal Cemetery at Ur, 2600–2400 BCE. The face is of 20 variously inlaid square shell plaques; edges made of small plaques and strips, some sculptured with an eye and some possibly with rosettes; on the back are three lines of shell triangular ornamental inlays.

Large double boat-shaped gold earring from Ur, 2500 BCE.

Jewelry and ornamentation from Royal Cemetery at Ur, 2600 BCE. Gold earring shaped as double boats, gold comb, necklace of alternating beads of cornelian and gold; 81 of cornelian; 72 of plain gold; 9 segmented gold; gold round beads. Collar of gold and lapis lazuli alternating triangles; pierced for three strings. Gold ribbon from a headdress.
They were one of the first Bronze Age people in the world. Palaces and temples were decorated with copper, bronze, and gold; copper, bronze, and iron were used for armor and weaponry such as swords, daggers, spears, and maces.
External Stories and Videos

Listen: Ancient Poetry of Babylon
SOAS University of London
Hear ancient Babylonian and Assyrian poetry and literature in the original language.

Pyramids: Stairway to the Gods
Sally Mallam, Human Journey
Found on at least three continents, pyramids are yet another example of how humans expressed their place in a three-tiered universe.

